SSH (Secure Shell) is a cryptographic network protocol
SSH (Secure Shell) is a cryptographic network protocol used for secure communication between computers and servers. It allows you to establish a secure data transfer channel over an unsecured network by connecting an SSH client application to an SSH server. SSH is primarily used for remote login and remote command execution, as well as secure file transfer (SFTP, SCP).
SSH authentication is performed using public key cryptography, which ensures that the identity of the network computer and the user is verified. This protocol replaces older and less secure remote shell protocols such as Telnet, rlogin, and rsh.

-
- May 17, 2025 - 1 min read 18
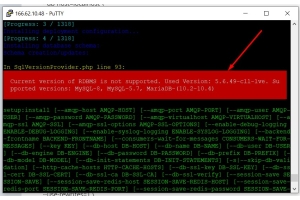
Microsoft Windows operating systems use the PuTTY program to establish SSH connections. If you experience connectivity issues, you can adjust PuTTY's configuration to help keep connections alive. To do this, follow these steps:
- Start PuTTY.
- Load your connection session.
- In the Category pane, click Connection.
- Under Sending of null packets to keep session active, in the Seconds between keepalives, type 240.
Note
With this configuration, PuTTY sends a packet to the server every 240 seconds (4 minutes) to keep the connection alive.
- In the Category pane, click Session.
- Click Save.
- Connect to your account and monitor the connection. If it still drops, gradually decrease the keepalive interval until the connection is stable.
Link: PuTTY






Login and Registration Form